Geschreven door: Charlotte de Deugd
Gepubliceerd op: september 2025
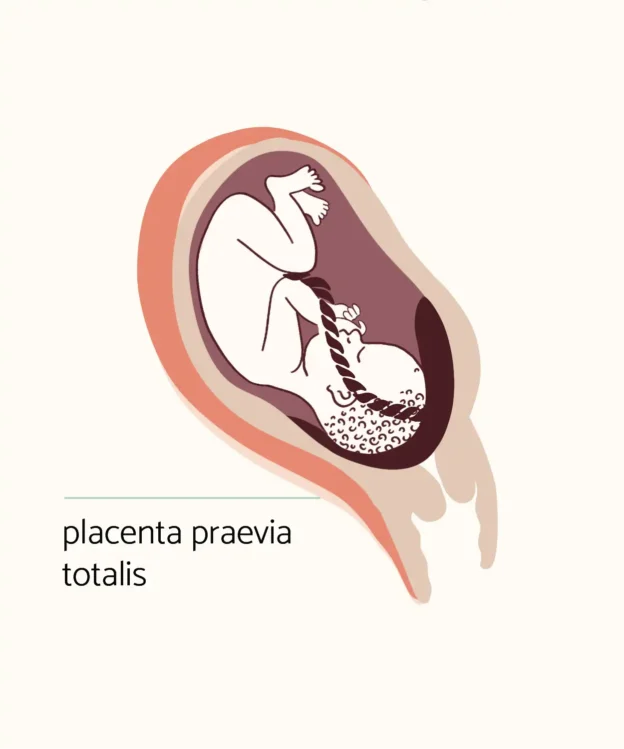
Een placenta praevia is een placenta die (gedeeltelijk) voor de inwendige opening van de baarmoedermond ligt. Deze aandoening komt voor 1 op de 111 tot 333 vrouwen ten tijde van de bevalling. De diagnose wordt gesteld met een inwendige echo. Als bij de 20 weken echo de placenta volledig, deels of dichtbij de inwendige opening van de baarmoeder ligt, maakt de echoscopist bij 30 tot 32 weken opnieuw een echo om de placentaligging te bekijken. Als de placencenta nog steeds laag ligt neemt het ziekenhuis de zwangerschapszorg over. Aan de hand van de afstand van de placenta tot het ostium internum, maakt de verloskundige of gynaecoloog de inschatting hoe veilig het is en hoe groot de kans van slagen is op een vaginale bevalling.
Wanneer spreek je precies van een placenta praevia en welke vormen zijn er? Hoe wordt een placenta praevia gediagnosticeerd? Welke factoren dragen bij aan het ontwikkelen van een placenta praevia? Wat zijn mogelijke risico’s van een placenta praevia? Wat is het huidige beleid qua vaginale bevalling versus een keizersnede en de timing hiervan? En wat is de onderbouwing van het beleid? In dit artikel besteden we aandacht aan deze vragen rondom placenta praevia.
Anderson-Bagga, F. M., & Sze, A. (2023). Placenta Previa. In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing. Geraadpleegd via NCBI Bookshelf: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539818/
Anne Rose S, A., & Gopalan, U. (2015). Correlation of maternal age with placenta previa. International Journal of Medical Research and Review, 3(9), 914-918. https://doi.org/10.17511/ijmrr.2015.i9.171
Baldwin HJ, Patterson JA, Nippita TA, Torvaldsen S, Ibiebele I, Simpson JM, Ford JB. Antecedents of Abnormally Invasive Placenta in Primiparous Women: Risk Associated With Gynecologic Procedures. Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Feb;131(2):227-233. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000002434. PMID: 29324602.
de Barros VIPVL, Igai AMK, Baptista FS, Bortolotto MRFL, Peres SV, Francisco RPV. Venous thromboembolism risk score during hospitalization in pregnancy: results of 10694 prospective evaluations in a clinical trial. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2023 Jun 10;78:100230. doi: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2023.100230. PMID: 37307627; PMCID: PMC10276210.
Cresswell JA, Ronsmans C, Calvert C, Filippi V. Prevalence of placenta praevia by world region: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Trop Med Int Health. 2013 Jun;18(6):712-24. doi: 10.1111/tmi.12100. Epub 2013 Apr 1. PMID: 23551357.
Faiz AS & Ananth CV (2003) Etiology and risk factors for placenta previa: an overview and meta-analysis of observational studies. Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine 13, 175–190.
Federatie Medisch Specialiseren. (2016, 21 april). Trombo-embolie bij zwangerschap en postpartum. In Richtlijnendatabase: Antitrombotisch beleid – Preventie VTE in de verloskunde. Geraadpleegd van https://richtlijnendatabase.nl/richtlijn/antitrombotisch_beleid/preventie_vte_in_de_verloskunde/trombo-embolie_bij_zwangerschap_en_postpartum.html
Francois K, Johnson JM, Harris C. Is placenta previa more common in multiple gestations? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003 May;188(5):1226-7. doi: 10.1067/mob.2003.334. PMID: 12748486.
Hu H, Wang L, Gao J, Chen Z, Chen X, Tang P, Zhong Y. Risk factors of severe postpartum hemorrhage in pregnant women with placenta previa or low-lying placenta: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024 Oct 15;24(1):674. doi: 10.1186/s12884-024-06876-3. PMID: 39407169; PMCID: PMC11475889.
Jansen CHJR, van Dijk CE, Kleinrouweler CE, Holzscherer JJ, Smits AC, Limpens JCEJM, Kazemier BM, van Leeuwen E, Pajkrt E. Risk of preterm birth for placenta previa or low-lying placenta and possible preventive interventions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 2;13:921220. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.921220. PMID: 36120450; PMCID: PMC9478860.
Jauniaux ERM, Alfirevic Z, Bhide AG, Belfort MA, Burton GJ, Collins SL, Dornan S, Jurkovic D, Kayem G, Kingdom J, Silver R, Sentilhes L on behalf of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. Placenta Praevia and Placenta Accreta: Diagnosis and Management. Green-top Guideline No. 27a. BJOG2018
Jenabi E, Bashirian S, Khoshravesh S. The association between of placenta previa and congenital abnormalities: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMC Pediatr. 2023 Nov 30;23(1):606. doi: 10.1186/s12887-023-04433-z. PMID: 38031046; PMCID: PMC10687781.
Jenabi E, Salimi Z, Bashirian S, Khazaei S, Ayubi E. The risk factors associated with placenta previa: An umbrella review. Placenta. 2022 Jan;117:21-27. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2021.10.009. Epub 2021 Oct 20. PMID: 34768164.
Karimi A, Sayehmiri K, Vaismoradi M, Dianatinasab M, Daliri S. Vaginal bleeding in pregnancy and adverse clinical outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2024 Dec;44(1):2288224. doi: 10.1080/01443615.2023.2288224. Epub 2024 Feb 2. PMID: 38305047.
King LJ, Dhanya Mackeen A, Nordberg C, Paglia MJ. Maternal risk factors associated with persistent placenta previa. Placenta. 2020 Sep 15;99:189-192. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2020.08.004. Epub 2020 Aug 6. PMID: 32854040.
Kohari KS, Roman AS, Fox NS, Feinberg J, Saltzman DH, Klauser CK, Rebarber A. Persistence of placenta previa in twin gestations based on gestational age at sonographic detection. J Ultrasound Med. 2012 Jul;31(7):985-9. doi: 10.7863/jum.2012.31.7.985. PMID: 22733846.
Korosec S, Ban Frangez H, Verdenik I, Kladnik U, Kotar V, Virant-Klun I, Vrtacnik Bokal E. Singleton pregnancy outcomes after in vitro fertilization with fresh or frozen-thawed embryo transfer and incidence of placenta praevia. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:431797. doi: 10.1155/2014/431797. Epub 2014 Apr 13. PMID: 24822209; PMCID: PMC4005152.
Kwee, A. (2005). Caesarean section in the Netherlands. Policy, prevention and long-term consequences. [Doctoral thesis 1 (Research UU / Graduation UU), Utrecht University]. Febodruk.
Lauria MR, Smith RS, Treadwell MC, Comstock CH, Kirk JS, Lee W, Bottoms SF. The use of second-trimester transvaginal sonography to predict placenta previa. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 1996 Nov;8(5):337-40. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-0705.1996.08050337.x. PMID: 8978009.
Leerentveld RA, Gilberts EC, Arnold MJ, Wladimiroff JW. Accuracy and safety of transvaginal sonographic placental localization. Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Nov;76(5 Pt 1):759-62. doi: 10.1097/00006250-199011000-00006. PMID: 2216220.
Lipa M, Goławski K, Kosiński P, Wielgoś M, Bomba-Opoń D. Placenta praevia - does it really affect intrauterine fetal growth? J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022 Oct;35(20):3898-3902. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2020.1843152. Epub 2020 Nov 13. PMID: 33183106.
NVOG richtlijn bloedverlies in de tweede helft van de zwangerschap, 2008
NVOG Module Modus partus bij placenta praevia marginalis, 2015
Oppenheimer L, Holmes P, Simpson N, Dabrowski A. Diagnosis of low-lying placenta: can migration in the third trimester predict outcome? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2001 Aug;18(2):100-2. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-0705.2001.00450.x. PMID: 11529986.
Oyelese Y, Shainker SA. Placenta Previa. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2025 Mar 1;68(1):86-92. doi: 10.1097/GRF.0000000000000911. Epub 2024 Dec 10. PMID: 39654466.
Parazzini F, Tozzi L, Bianchi S. Pregnancy outcome and uterine fibroids. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2016 Jul;34:74-84. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2015.11.017. Epub 2015 Nov 25. PMID: 26723475.
Pinton A, Deneux-Tharaux C, Seco A, Sentilhes L, Kayem G; PACCRETA Study Group. Incidence and risk factors for severe postpartum haemorrhage in women with anterior low-lying or praevia placenta and prior caesarean: Prospective population-based study. BJOG. 2023 Dec;130(13):1653-1661. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.17554. Epub 2023 May 24. PMID: 37226308.
Rathbun KM, Hildebrand JP. Placenta Abnormalities. [Updated 2022 Oct 17]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459355/
Roberts, C.L., Algert, C.S., Warrendorf, J., Olive, E.C., Morris, J.M. and Ford, J.B. (2012), Trends and recurrence of placenta praevia: A population-based study. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol, 52: 483-486. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1479-828X.2012.01470.x
Romundstad LB, Romundstad PR, Sunde A, von Düring V, Skjaerven R, Vatten LJ. Increased risk of placenta previa in pregnancies following IVF/ICSI; a comparison of ART and non-ART pregnancies in the same mother. Hum Reprod. 2006 Sep;21(9):2353-8. doi: 10.1093/humrep/del153. Epub 2006 May 25. PMID: 16728419.
Ruiter L, Eschbach SJ, Burgers M, Rengerink KO, van Pampus MG, Goes BY, Mol BW, Graaf IM, Pajkrt E. Predictors for Emergency Cesarean Delivery in Women with Placenta Previa. Am J Perinatol. 2016 Dec;33(14):1407-1414. doi: 10.1055/s-0036-1584148. Epub 2016 May 16. PMID: 27183001.
Schwartz A, Chen D, Shinar S, Agrawal S, Yogev Y. Timing of cesarean delivery in women with uncomplicated placenta previa. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022 Dec;35(26):10559-10564. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2022.2134772. Epub 2022 Oct 19. PMID: 36261133.
SCOG, Guideline No. 402: Diagnosis and Management of Placenta Previa
Jain, VenuBos, HayleyBujold, Emmanuel et al.
Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada. (2020) Volume 42, Issue 7, 906 - 917.e1
Senkoro EE, Mwanamsangu AH, Chuwa FS, Msuya SE, Mnali OP, Brown BG, Mahande MJ. Frequency, Risk Factors, and Adverse Fetomaternal Outcomes of Placenta Previa in Northern Tanzania. J Pregnancy. 2017;2017:5936309. doi: 10.1155/2017/5936309. Epub 2017 Feb 21. PMID: 28321338; PMCID: PMC5339534.
Silver, Robert M. MD. Abnormal Placentation: Placenta Previa, Vasa Previa, and Placenta Accreta. Obstetrics & Gynecology 126(3):p 654-668, September 2015. | DOI: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000001005
Sultan, A. A., West, J., Tata, L. J., Fleming, K. M., Nelson-Piercy, C., & Grainge, M. J. (2013). Risk of first venous thromboembolism in pregnant women in hospital: population based cohort study from England. Bmj, 347.
Taipale P, Hiilesmaa V, Ylöstalo P. Transvaginal ultrasonography at 18-23 weeks in predicting placenta previa at delivery. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 1998 Dec;12(6):422-5. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-0705.1998.12060422.x. PMID: 9918091.
Toscano, Marika MD; Royzer, Rebecca BA; Castillo, Daniel MLIS; Li, Dongmei PhD; Poleshuck, Ellen PhD. Prevalence of Depression or Anxiety During Antepartum Hospitalizations for Obstetric Complications: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Obstetrics & Gynecology 137(5):p 881-891, May 2021. | DOI: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000004335
Williamson SP, Moffitt RL, Broadbent J, Neumann DL, Hamblin PS. Coping, wellbeing, and psychopathology during high-risk pregnancy: A systematic review. Midwifery. 2023 Jan;116:103556. doi: 10.1016/j.midw.2022.103556. Epub 2022 Nov 14. PMID: 36427386.
Wing DA, Paul RH, Millar LK. Management of the symptomatic placenta previa: a randomized, controlled trial of inpatient versus outpatient expectant management. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1996 Oct;175(4 Pt 1):806-11. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(96)80003-2. PMID: 8885726.
Zlatnik, M. G., Cheng, Y. W., Norton, M. E., Thiet, M. P., & Caughey, A. B. (2007). Placenta previa and the risk of preterm delivery. Journal of Maternity, Fetal & Neonatal Medicine, 20(9), 719–723. https://doi.org/10.1080/14767050701673175